Turns out that when your mother told you to stop sitting near the TV or you might need glasses, she was onto something.
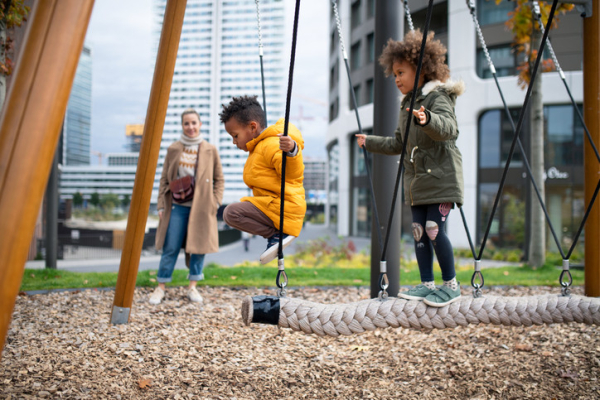
Myopia, or nearsightedness, is a growing problem worldwide. While a nearsighted child can see close objects clearly, more distant objects look blurry. Part of this growing problem, according to experts, is that children are spending too much time indoors looking at things close to them rather than going outside and looking at things that are far away.
What is nearsightedness?
Nearsightedness is very common, affecting about 5% of preschoolers, 9% of school-age children, and 30% of teens. But what worries experts is that over the last few decades its global prevalence has doubled — and during the pandemic, eye doctors have noticed an increase in myopia.
Nearsightedness happens when the eyeball is too large from front to back. Genes play a big role, but growing research shows that there are developmental factors. The stereotype of the nerd wearing glasses actually bears out; research shows that the more years one spends in school, the higher the risk of myopia. Studies also show, even more reliably, that spending time outdoors can decrease a child’s risk of developing myopia.
Why would outdoor time make a difference in nearsightedness?
While surprising, this actually makes some sense. As children grow and change, their lifestyles affect their bodies. A child who is undernourished, for example, may not grow as tall as they might have if they had better nourishment. A child who develops obesity during childhood is far more likely to have lifelong obesity. And the eyes of a child who is always looking at things close to him or her might adjust to this — and lose some ability to see far away.
Nearsightedness has real consequences. Not only can it cause problems with everyday tasks that require you to see more than a few feet away, such as school or driving, but people with myopia are at higher risk of blindness and retinal detachment. The problems can’t always be fixed with a pair of glasses.
What can parents do?
- Make sure your child spends time outdoors regularly — every day, if possible. That’s the best way to be sure that they look at things far away. It’s also a great way to get them to be more active, get enough Vitamin D, and learn some important life skills.
- Try to limit the amount of time your child spends close to a screen. These days, a lot of schoolwork is on screens, but children are also spending far too much of their playtime on devices rather than playing with toys, drawing, or other activities. Have some ground rules. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends no more than two hours of entertainment media a day, and has a great Family Media Plan to help families make this happen.
- Have your child’s vision checked regularly. Most pediatricians do regular vision screening, but it is important to remember that basic screening can miss vision problems. It’s a good idea for your child to have a full vision examination from an ophthalmologist or an optometrist by kindergarten.
- Call your pediatrician or child’s eye doctor if you notice signs of a possible vision problem, such as
- sitting close to the television or holding devices close to the face
- squinting or complaining of any difficulty seeing
- not being able to identify objects far away (when you go for walks, play I Spy and point to some far-away things!)
- avoiding or disliking activities that involve looking close, like doing puzzles or looking at books, which can be a sign of hyperopia (farsightedness)
- tilting their head to look at things
- covering or rubbing an eye
- one eye that turns inward or outward.
If you have any questions or concerns about your child’s vision, talk to your pediatrician.
Follow me on Twitter @drClaire
About the Author

Claire McCarthy, MD, Senior Faculty Editor, Harvard Health Publishing
Claire McCarthy, MD, is a primary care pediatrician at Boston Children’s Hospital, and an assistant professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School. In addition to being a senior faculty editor for Harvard Health Publishing, Dr. McCarthy … See Full Bio View all posts by Claire McCarthy, MD